According to the latest statistics from the United Nations, India has officially become the world’s most populous country. As of 2023, the population of India stands at 1.43 billion, which is on par with China. The United States is the third most populous country with 340 million citizens, followed by Indonesia with 278 million, Pakistan with 240 million, Nigeria with 224 million, Brazil with 216 million, Bangladesh with 173 million, and Russia with 144 million. This data is expected to have significant implications on the global economy, politics, and resources distribution.
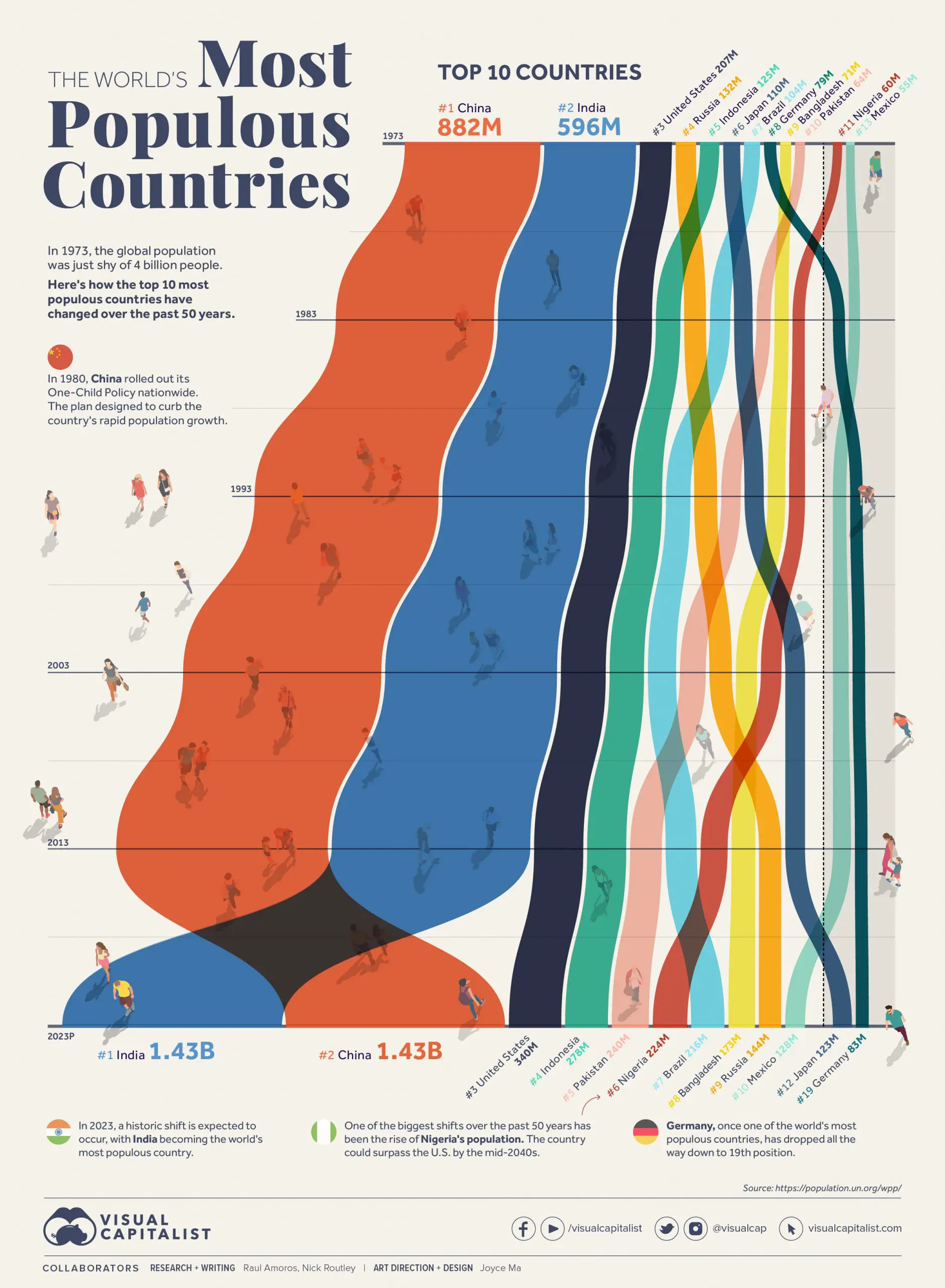
The population growth in India has been driven by a combination of factors such as improved healthcare and sanitation, reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy. This has led to a decline in the death rate and an increase in the birth rate. However, India also faces several challenges related to population growth, such as increased pressure on resources, infrastructure and services, as well as potential for strain on the environment.
The population growth in China, on the other hand, has been slowed down by the implementation of the “One Child Policy” which was in place from 1979 to 2015. However, the policy has also led to a rapidly aging population and a gender imbalance as a result of a cultural preference for male children.
The United States, with a population of 340 million, is the third most populous country in the world. The country’s population growth has been driven by both natural increase and immigration. The US population is projected to continue to grow, but at a slower rate than in the past.
Indonesia, with a population of 278 million, is the fourth most populous country in the world. The country’s population growth has been driven by a combination of factors such as improved healthcare, reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy. However, like India, it also faces several challenges related to population growth, such as increased pressure on resources, infrastructure, and services.
Pakistan, with a population of 240 million, is the fifth most populous country in the world. The country’s population growth has been driven by a combination of factors such as improved healthcare, reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy. However, like other countries, it also faces several challenges related to population growth, such as increased pressure on resources, infrastructure, and services.
Nigeria, with a population of 224 million, is the sixth most populous country in the world. The country’s population growth has been driven by a combination of factors such as improved healthcare, reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy. However, like other countries, it also faces several challenges related to population growth, such as increased pressure on resources, infrastructure, and services.
Brazil, with a population of 216 million, is the seventh most populous country in the world. The country’s population growth has been driven by a combination of factors such as improved healthcare, reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy. However, like other countries, it also faces several challenges related to population growth, such as increased pressure on resources, infrastructure, and services.
Bangladesh, with a population of 173 million, is the eighth most populous country in the world. The country’s population growth has been driven by a combination of factors such as improved healthcare, reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy. However, like other countries, it also faces several challenges related to population growth, such as increased pressure on resources, infrastructure, and services.
Russia, with a population of 144 million, is the ninth most populous country in the world. The country’s population growth has been driven by a combination of factors such as improved healthcare, reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy. However, like other countries, it also faces several challenges related to population growth, such as increased pressure on resources, infrastructure, and services.
Overall, it’s clear that population growth has significant implications for the global economy, politics, and resources distribution. Governments and international organizations will need to work together to address these challenges and ensure that the needs of all citizens are met.
Test















